Nicolaus Copernicus

Nicolas Copernicus was born on February 29, 1473, in Thorn, Poland. He was the son of a wealthy merchant and the youngest of four children. His father died in 1483, and he was raised by his uncle, a bishop of the Catholic Church. Since his uncle was a bishop, he facilitated his advancement in the church. His uncle arranged his election as a canon and from his new position in the church he was secured pay for life. He began his education at the University of Krakow, where he studied canon law, mathematics and astronomy. At the age of eighteen, Nicolas traveled to Italy off the money saved from his canon position to attend college. He studied law, mathematics, and medicine at the universities of Bologna, Padua, and Ferrara.
While attending the University of Bologna, Copernicus lived with the astronomy professor Domenico Maria Novara. During his stay with Novara, his gained a greater interest in a astronomy and made his first astronomical observations. As he made more observations, he began to question the ideas of the time. At the time, most people believed that the Earth was in the center of the universe and that the all the planets, stars, and sun revolved around it. This idea is known as the Ptolemaic Theory. Ptolemy, a great Greek astrologer, mathematician, and thinker, made this model of the Solar System. Copernicus was the first person to challenge Ptolemy and his theory. Through careful observation, Copernicus noted a major problem with Ptolemy’s model. The mathematical issue he noticed was that occasionally the planets would travel backwards through the sky. This is known as retrograde motion.
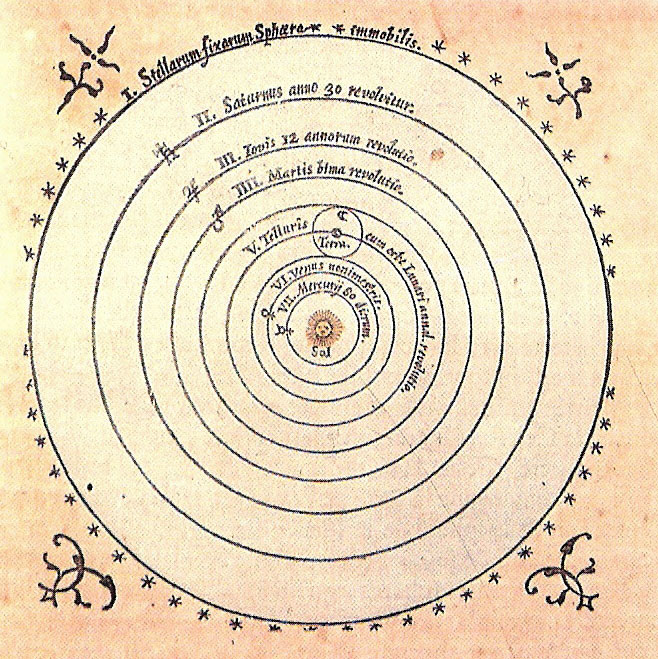
In 1514 after moving back to Poland, Copernicus distributed the first handwritten copies of his book to his friends. In his book he purposed that the Earth was not in ne center of the universe but instead the sun was. The principles of his sun-centered astronomy became known as heliocentric astronomy. His book also stated that the rotation of the Earth around the sun accounted for the rising and setting of the sun, movement of the stars, and the changing season. Finally his book also explained that the Earth’s motion through space caused the retrograded motion of the planets. Copernicus did not publish his book, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium, until he was on his deathbed. He waited to publish his book because he knew it was against the church and he would be a heretic. Fortunately after his death on May 24, 1543, the worst punishment the church could give was putting his book on the Index, the naughty book list.
Nicolas Copernicus’s work is considered the defining aspect of the scientific revolution, because his work simulated further scientific investigations. He was the first person to combine mathematics, physics, and cosmology to create a complete general system of the solar system. He disproved that the Earth was in the center of the Universe, but only had the idea of the heliocentric model. His ideas were not fully accepted until later astronomers like Galileo, Kepler, and Newton developed and refinded his work. Today our current model is basically the same as Copernicus’s original design. There have been a few new discoveries that have been added on to his model, but the overall idea is the same and is still often refered to as the Copernican model. Copernicus changed the view of astronomy and the universe at the time. Due to his discoveries and work in the field of astronomy, he is considered the father of modern astronomy.
While attending the University of Bologna, Copernicus lived with the astronomy professor Domenico Maria Novara. During his stay with Novara, his gained a greater interest in a astronomy and made his first astronomical observations. As he made more observations, he began to question the ideas of the time. At the time, most people believed that the Earth was in the center of the universe and that the all the planets, stars, and sun revolved around it. This idea is known as the Ptolemaic Theory. Ptolemy, a great Greek astrologer, mathematician, and thinker, made this model of the Solar System. Copernicus was the first person to challenge Ptolemy and his theory. Through careful observation, Copernicus noted a major problem with Ptolemy’s model. The mathematical issue he noticed was that occasionally the planets would travel backwards through the sky. This is known as retrograde motion.
In 1514 after moving back to Poland, Copernicus distributed the first handwritten copies of his book to his friends. In his book he purposed that the Earth was not in ne center of the universe but instead the sun was. The principles of his sun-centered astronomy became known as heliocentric astronomy. His book also stated that the rotation of the Earth around the sun accounted for the rising and setting of the sun, movement of the stars, and the changing season. Finally his book also explained that the Earth’s motion through space caused the retrograded motion of the planets. Copernicus did not publish his book, De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium, until he was on his deathbed. He waited to publish his book because he knew it was against the church and he would be a heretic. Fortunately after his death on May 24, 1543, the worst punishment the church could give was putting his book on the Index, the naughty book list.
Nicolas Copernicus’s work is considered the defining aspect of the scientific revolution, because his work simulated further scientific investigations. He was the first person to combine mathematics, physics, and cosmology to create a complete general system of the solar system. He disproved that the Earth was in the center of the Universe, but only had the idea of the heliocentric model. His ideas were not fully accepted until later astronomers like Galileo, Kepler, and Newton developed and refinded his work. Today our current model is basically the same as Copernicus’s original design. There have been a few new discoveries that have been added on to his model, but the overall idea is the same and is still often refered to as the Copernican model. Copernicus changed the view of astronomy and the universe at the time. Due to his discoveries and work in the field of astronomy, he is considered the father of modern astronomy.
Quote from Nicolaus Copernicus